The Synergy Between Craftsmanship and Sustainability: Innovations Promoting Ecological Practices in Nigerian Artisan Production

Embracing Environmental Responsibility
The current landscape of artisan production in Nigeria reflects a notable shift towards a holistic integration of cultural heritage and ecological mindfulness. This movement highlights the profound commitment of artisans to not only craft beauty but also safeguard the environment through their practices. As artisans merge their traditional skills with sustainable approaches, they pave the way for a new paradigm in craftsmanship that resonates deeply with the pressing environmental needs of our time.
Numerous examples manifest this trend throughout Nigeria, showcasing the potential of eco-conscious craftsmanship:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Artisans are increasingly utilizing materials such as organic cotton, bamboo, and reclaimed wood. By choosing these renewable resources, they reduce the industry’s carbon footprint. For instance, local fashion designers are adopting fabrics dyed with natural pigments derived from indigenous plants, which not only brings vibrant colors but also eliminates the pollution often associated with synthetic dyes.
- Waste Reduction: As part of their creative process, artisans are employing innovative techniques to minimize waste. Tailors, for example, are using remnants from previous projects to create new designs, resulting in unique pieces that carry stories of both creativity and conservation. In some cases, artisans transform discarded materials into intricate mosaics or functional art, demonstrating that waste can indeed be a resource.
- Community Involvement: Collaborative efforts are enhancing local economies while fostering a culture of sustainability. Community projects, such as workshops where skills are shared and sustainable practices are taught, empower artisans and residents alike. For instance, initiatives in cities like Lagos promote skill-sharing among craftspeople, encouraging the adoption of sustainable practices while creating economic opportunities. Such collaborations often lead to cooperative galleries that not only display their collective work but also educate the public about sustainable craftsmanship.
This progressive movement is not merely reshaping artisan production; it is generating a ripple effect that encourages consumers to be more conscious of their purchases. Many Nigerians are now more inclined to support local artisans whose values align with their own, fostering a market that prizes sustainability as much as it does creativity.
Furthermore, the incorporation of technology plays a vital role in this evolution. For example, some artisans are utilizing digital platforms to reach broader audiences, sharing their unique stories and sustainable practices with people far beyond Nigeria’s borders. This symbiotic relationship between tradition and innovation is redefining what it means to be a craftsman in the 21st century.
In conclusion, the merging of craftsmanship and sustainability in Nigeria is a vital movement that reflects a broader, global shift toward responsible production methodologies. As artisans continue to explore innovative strategies and practices that honor their cultural heritage while embracing ecological responsibility, they are not only redefining the landscape of local craftsmanship but are also inspiring future generations to consider the environmental impacts of their creations. This resilient spirit of artisans offers a compelling narrative of hope and creativity, inviting us all to engage with the values of sustainability in our daily lives.
RECOMMENDED: Check out this similar article
Innovative Practices Transforming Artisan Production
Nigeria’s rich tapestry of craftsmanship is becoming ever more intertwined with sustainable practices. This symbiotic relationship is not just a trend; it is a transformative movement that addresses pressing environmental challenges while empowering local artisans. Within this dynamic landscape, several key practices are emerging, highlighting the ingenuity of Nigerian artisans and their commitment to sustainability.
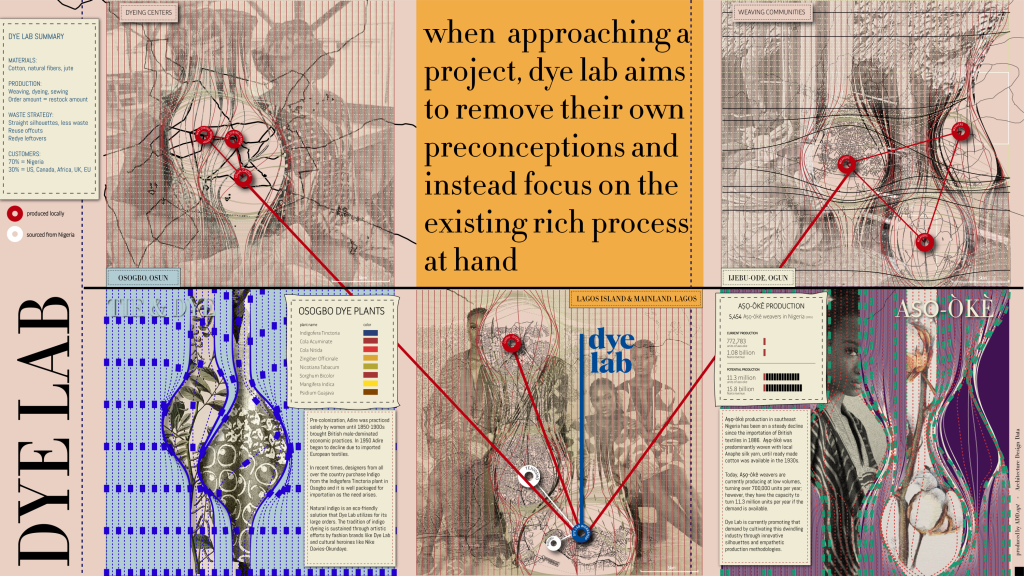
Utilization of Local Resources: One of the most notable innovations within Nigerian artisan production is the emphasis on locally sourced materials. This approach not only minimizes transportation emissions but also helps revive local economies. For instance, artisans in the northern regions are using adire, a traditional fabric made from indigo dye that is both biodegradable and historically significant. By supporting indigenous harvesting techniques and local dyeing methods, artisans weave cultural heritage into their sustainable practices, promoting a connection to their landscapes.
The Role of Traditional Knowledge: Traditional knowledge is being revitalized in innovative ways. Craftspeople are returning to age-old techniques that are eco-friendly, such as basket weaving and pottery. These methods, which utilize natural materials and labor-intensive processes, carry a low carbon footprint compared to mass-produced alternatives. Moreover, communities that engage in these practices often emphasize the importance of storytelling in their craft, thereby fostering a deep respect for the environment and the cultural narratives interwoven within it.
Innovative Product Design: The push for sustainability has also influenced product design. Artisans now create items that are not only functional but also designed for longevity. A significant example lies in the furniture-making sector, where artisans are crafting elegant pieces from reclaimed or sustainably harvested wood. This practice reduces deforestation while producing unique, high-quality items that appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Furthermore, the trend of designing multi-functional products reflects a growing awareness of resourcefulness, as seen in the creation of furniture that serves multiple purposes.
In light of these innovations, several key components underscore the movement towards sustainable craftsmanship in Nigeria:
- Community Engagement: Local workshops and artisan guilds are facilitating knowledge exchange, encouraging artisans to share sustainable practices. These gatherings do not only strengthen community bonds but also spread awareness about ecological responsibilities.
- Market Accessibility: Online platforms and social media channels are enabling artisans to reach wider markets while connecting them with consumers who value sustainability. By utilizing e-commerce, artisans can share their stories and maintain transparency about their production methods, catering to a growing audience that prioritizes ethical consumption.
- Government Policies: Supportive government initiatives aimed at fostering local craft industries are crucial for sustainability. Programs focused on training artisans in eco-friendly techniques can enhance productivity while fortifying Nigeria’s artisanal heritage.
The emergence of these innovative practices in Nigerian artisan production showcases a proactive stance towards sustainability, reflecting a broader push for ecological consciousness in the face of environmental degradation. As artisans continue to balance tradition with innovation, they light the way for future generations, proving that craftsmanship and sustainability can indeed coexist harmoniously.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Quality | Artisans focus on high-quality materials, creating products that are not only durable but also aesthetically pleasing. |
| Environmental Awareness | Nigerian artisans are pioneering sustainable practices that minimize waste and utilize locally sourced materials, promoting ecological balance. |
| Cultural Preservation | Through their crafts, artisans are preserving traditional techniques while adapting them to new sustainable methods. |
| Community Empowerment | These innovations create job opportunities, thereby strengthening local economies and fostering community development. |
In recent years, innovation in Nigerian artisan production has emerged as a beacon of hope for sustainable entrepreneurship. Artisans are now leveraging advanced techniques and seeking to integrate eco-friendly materials into their production processes. This merger of art and ecological responsibility fosters a unique crafting philosophy that resonates deeply within both local and global markets. Moreover, consumers are increasingly drawn to products that not only tell a story but also honor the environment. By choosing artisan goods, buyers contribute to a narrative of sustainability, thus fueling a sector that invests in the future while celebrating the rich tapestry of Nigerian heritage. The shift toward sustainability transcends mere production; it is a movement that embraces ethical responsibility and the rejuvenation of cultural practices interwoven with environmental respect.
SEE ALSO: Click here to read another article
Eco-Conscious Collaborations and Education
As the drive towards sustainability gains momentum, collaborations between artisans, environmental organizations, and educational institutions are proving to be pivotal in enhancing the ecological footprint of Nigeria’s craft sector. These partnerships not only amplify the voices of artisans but also facilitate the exchange of innovative ideas, techniques, and sustainable practices.
Collaborative Networking: A growing number of artisan collectives are emerging, bringing together skilled craftspeople to share resources and practices. These networks focus on sustainability through collaborative projects, where artists work side by side to create hybrid products that reflect various cultural influences while adhering to environmental standards. For instance, initiatives like the Nigerian Craft Fair showcase products that are either made from recycled materials or employ eco-friendly processes, thus inspiring artisans across the country to adopt sustainable methodologies.
Educational Workshops: Workshops led by sustainability experts and experienced artisans are becoming instrumental in the capacity-building efforts for craftsmen. These programs are designed to equip artisans with skills in sustainable sourcing, eco-friendly production methods, and waste reduction techniques. For example, in Lagos, the Centre for Sustainable Development offers training sessions for woodworkers on how to utilize non-timber materials, an approach that not only reduces deforestation but also introduces innovative crafting possibilities.
The Rise of Upcycling: A particularly compelling trend among Nigerian artisans is the rise of upcycling, where waste materials are creatively transformed into valuable products. This not only reduces landfill waste but also provides artisans with a unique opportunity to differentiate their products in the marketplace. From transforming discarded plastics into accessories to repurposing old fabric scraps into vibrant artworks, artisans are proving that sustainability can be synonymous with creativity and desirability. An interesting example can be observed in the coastal regions, where fishermen are turning their old nets into stylish bags, reflecting both innovation and environmental consciousness.
Sustainability in Textiles: The textile industry in Nigeria is also witnessing a shift towards sustainability. Artisans are increasingly exploring natural dyes extracted from local plants, which significantly reduces the harmful effects of chemical dyes on the environment. For instance, the use of plant-based dyes not only ensures biodegradable fabric but also promotes biodiversity as artisans cultivate particular plants for dyeing. This return to organic methods is not just a nod to sustainability; it enhances the richness of Nigeria’s textile heritage.
Empowerment Through Fair Trade: The concept of fair trade has also gained traction among Nigerian artisans. By ensuring that artisans receive a fair wage for their products, this model fosters economic empowerment and encourages them to invest more in sustainable practices. Organizations like Trade and Craft Network offer support by connecting artisans to global markets, ensuring their creations are sold in ethical spaces, thereby promoting both sustainable production and livelihoods.
The synergy between craftsmanship and sustainability in Nigeria is a multifaceted phenomenon fueled by collaborations and educational efforts. Through innovative practices and community engagement, artisans increasingly demonstrate that ecological consciousness can flourish alongside fine craftsmanship. The landscape is evolving, and as artisans embrace these innovations, they pave the way for a sustainable future that preserves cultural heritage while addressing contemporary environmental concerns.
CHECK OUT: Click here to explore more
Conclusion
In the realm of Nigerian artisan production, the dynamic intersection of craftsmanship and sustainability has emerged as a beacon of hope and innovation. As artisans embrace eco-friendly practices and partake in collaborative networks, they are not only showcasing their individual talents but also contributing to a collective movement that prioritizes environmental stewardship. This synergy marks a significant shift towards practices that honor both cultural heritage and ecological responsibility.
Through initiatives such as upcycling and the use of natural dyes, artisans are redefining traditional techniques, forging a path that resonates with modern sustainability trends while celebrating their rich artistic legacies. Moreover, fair trade conditions ensure that artisans are economically empowered, enabling them to support their communities and invest in greener production methods.
The ripple effect of these innovations extends beyond the confines of the artisan’s workshop; it stimulates local economies, promotes conservation efforts, and elevates Nigeria’s craft sector in global markets. The collaborative spirit rooted in education and environmental awareness is creating a robust framework for sustainable development in the arts, inspiring future generations to push the boundaries of creativity while committing to ecological practices.
As we witness this transformation, it becomes clear that the future of Nigerian craftsmanship is not merely about creating beautiful objects; it is about cultivating a sustainable ethos that honors the planet. Thus, as consumers and advocates for change, we are encouraged to delve deeper into the stories behind these artisanal creations, supporting those who strive to marry aesthetics with environmental integrity. The journey ahead holds tremendous potential for innovation, community empowerment, and the preservation of our planet’s resources, proving that sustainability is indeed a cornerstone of authentic craftsmanship.


